ECOTWIN
Analyze real ecosystems via their digital twins
Explore the ecological consequences of human interventions at the planning stage

WHAT IS ECOTWIN?
Three-dimensional terrain models Terrestrial and marine ecosystems Generic models of animals and plants Genotypes and phenotypes Sexual and asexual reproduction Nervous systems modeled by deep reinforcement learning Individual and lifelong learning Reward signal based on homeostasis

applications
Consequence analysis of human interventions in real ecosystems via fishing, forestry, agriculture, and urbanization Theoretical biology, including evolution and ethology Game theory and behavioral economics Video games Robotics
MASTER'S PROJECTS (FROM 2020-2021)

Lotka-Volterra dynamics
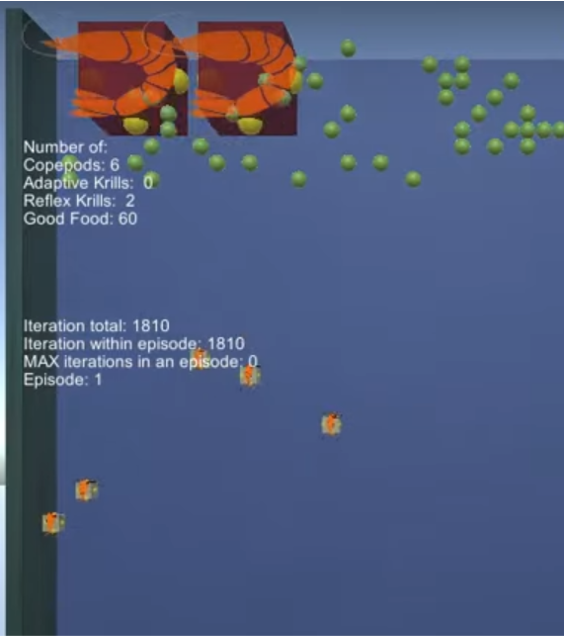
Diel vertical migration
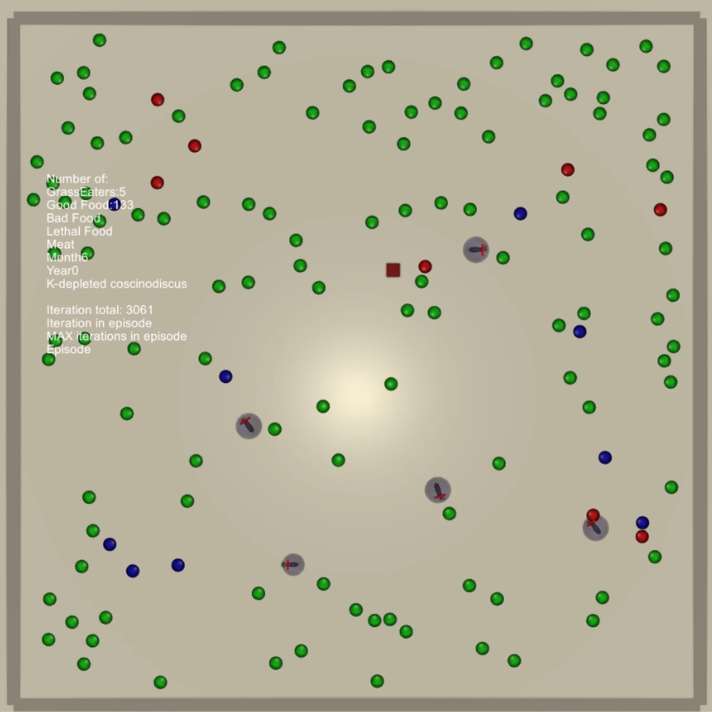
Evolution of reflexes
resources
VIDEOS
MSc thesis presentation (H. Glimmerfors, V. Skoglund)